Softwaretechnik / Software Engineering (Lecture)
| Course type | Lecture |
|---|---|
| Instructors | Prof. Dr. Andreas Podelski Dr. Bernd Westphal |
| Lecture | Recording ("as if" Tuesday, 14:00–16:00) Recording ("as if" Thursday, 12:00–14:00) |
| Exercise | Tuesday, 14:00–16:00 or 16:00 - 18:00 (bi-weekly), Live Online Tutorial Session |
| First session | Tutorial: tba. |
| Language of instruction | German (and English) |
| Credits | 6 |
| Exams | 2021-09-22, 9:00am, building 101 |
| Course Catalog | Softwaretechnik / Software Engineering - Vorlesung Softwaretechnik / Software Engineering - Übung |
Quicklinks: News - Online-ing - Formalia - Plan - Links & Literature
News
- 2021-10-11: The exam review takes place on Friday, 15th October (see below)
- 2021-09-17: Updated Errata/DE and Errata/EN (also see here) - short notice note: exam tasks will not be affected by this fix..
- 2021-08-03: Updated Errata/DE and Errata/EN (also see here).
- 2021-06-23: The exam date has come to our attention - see Formalia below.
- 2021-06-22: Change of plans: Maybe it is the least confusing approach to simply follow the numbers of 2019 and 2018, yet this comes at the price that the DE and EN track take different routes in a partial order on content. The DE track will do (A,B,C) in the upcoming lectures block and then (D,E,F) while the EN track will do (A,D,B) and then (C,E,F). All not harmful for the exercises, and in the end, we'll all be in sync again (cf. forum post on upcoming lectures block).
- 2021-04-22: Tutorial groups will be announced soon.
- 2021-04-22: If you missed the submission deadline for Exercise Sheet 0 and still want to be assigned to a tutorial group, consider to submit to the "dummy exercise" in the ILIAS until tomorrow noon to express this wish to be assigned.
- 2021-04-19: Lecture 1 and Exercise Sheet 0 online (see plan below).
- 2021-04-13: oh, that got resolved quickly, so: ILIAS is here. The regular way to join the module is via the coupled HISinOne course (or with this Direct Access Link if all else fails).
- 2021-04-13: homepage online, ILIAS not yet (technical issues with HIS/ILIAS coupling, it seems).
Online-ing
This season's "online-ing" of the Softwaretechnik / Software Engineering course is constructed around what we could call the "as if"-principle: "As if" we were having in-class sessions following the usual rhythm of lectures, exercises, and tutorials yet unfortunately they do not take place in-class.
Meaning:
- We have a schedule with lecture days and their planned topics, and since we cannot have in-class lectures, we will be using lecture recordings from earlier seasons.
So if you visit this homepage (or the ILIAS module) at a lecture day and time (as given by the schedule below), you will find a new recordings and PDFs with the annotated slides. (Actually, we will upload groups of two to four lectures and PDFs for one exercise sheet (see dependency illustration below) at once together with the first lecture of the group. It is then left at your discretion to choose the studying schedule that works best for you, be it "one lecture per lecture day, 'as if' we had in-class sessions and you just could not make it to the classroom", or more, or less.)
Questions go to an ILIAS forum. - The lectures are accompanied by exercises as usual, each block of two to four lectures has one exercise sheet. In most cases, the first exercise can be done with input from the first lecture (see dependency illustration below). So again: you will find your schedule (same as in in-class seasons).
- The exercises are accompanied by tutorial sessions. About every second week (only disturbed by public holidays and breaks) we will have live online tutorial sessions in a video meeting per tutorial group (accessible via ILIAS).
The tutorial sessions address the aspect that Software-Engineering is for a very good part about people interacting with people (like clients with developers, like programmers with designers, like teams of requirements engineers, etc.; cf. [Ludewig, Lichter, 2008] for example) and that is what we practice and experience in the tutorial sessions: Usage of professional terminology to efficiently and effectively communicate with (other) software engineering professionals about software engineering problems and solutions.
There will be a fixed, uniform exercise submission deadline for all tutorial groups - the exact day/time of the tutorial session can be subject to some negotiation (here's at least one positive point of online-ing: we are not limited by availability of physical rooms). - Every other week, there will be written feedback on exercise solutions as usual, i.e., your friendly tutor will provide feedback on individual errors, mistakes, or misconceptions that are not covered by the discussions in the tutorial sessions. In other words: the feedback may not always be comprehensive without the input from the tutorial sessions (this was different in the emergency online-ing of the 2020 season where effort was shifted from live/online to comprehensive written feedback at the painful price of sacrificing much of the "for life" aspect).
- Note: Tutorial groups will be formed after submission of Exercise Sheet 0 (available Monday, 19th of April, the latest) and afterwards we will have fixed tutorial groups. Your tutor will be available for questions and concerns throughout the teaching period until the exam day.
- Overall, the course covers four, mostly self-contained topic areas (as explained in more detail in (the recording of) Lecture 1). Hence if you may need to skip some lectures or exercises (for whatever pandemic-induced or other reasons), it is well possible to re-join the course at the beginning of the next topic area and catch up with the missed content later.
The following illustration (click to enlarge) shows dependencies between exercise sheets and lectures and may be useful for your schedule planning. Principally, one would like to see each topic area closed with a corresponding tutorial session, yet the obstacles in form of public holidays does not always allow such clear splits:
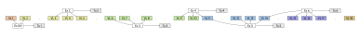
Your question about online-ing this course unanswered? Please contact us by mail or via the ILIAS forum.
Formalia
Prerequisites for exam admission, form of the final exam, and everything will be announced here and in the ILIAS forum.
Admission criteria
50% of the total (120) admission (or: good will) points are sufficient.
Exercise Submission Scheme
The exercise sheets are online early in order to allow you to be aware of the tasks while following the lecture. There will be an early/regular submission scheme following a pattern to be announced.
Please submit your solutions via ILIAS (log in with RZ account, not TF Pool account).
Note: The exercises will be rated on two scales: admission points (given your knowledge before the tutorial, how sensible is your proposal; "good will rating", "upper bound") and exam points (given the additional knowledge from the comments on your proposal and the tutorial, how many points would your proposal at least be worth in a written exam; "evil rating", "lower bound").
Exam
There will be a written exam:
- Date & time: 22.09.2021, 09.00 Uhr
- 90 min.
- Building 101
- Permitted in the exam:
max. 1 sheet of paper, max. size A4, max. 200g/qm quality, all sides may be used (written/printed/painted/...). - Cf. Klausurplan - it's one exam for all participants (BSc, MSc, ..., all).
- Last name starting with A to G: 14:00 to 14:30
- Last name starting with H to N: 14:30 to 15:00
- Last name starting with O to Z: 15:00 to 15:30
Slides, Exercises, and Recordings
Note: the following plan is tentative, that is, the assignment of events and topics to dates may be subject to (if possible: mild) changes.
- Errata/DE (Stand 2021-08-03), Errata/EN (Stand 2021-08-03).
- Tue, 20.4.: VL 01 "Introduction" - Exercise Sheet 0 online (submit via ILIAS)
Definitions of Software Engineering etc.; course content overview; formalia
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 22.4.: VL 02 "Software Metrics" - Exercise Sheet 1 online, additional file (submit via ILIAS)
Software metrics; properties of useful metrics; kinds of scales; examples: LOC and McCabe
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 27.4.: Live Online Tutorial 1
- Thu, 29.4.: VL 03a "More Metrics & Cost Estimation" - Exercise Sheet 2 online
Subjective metrics, Goal-Question-Metric approach; Cost and Deadlines, Expert and Algorithmic Cost Estimation
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 4.5.: VL 03b "Software Project Management"
Development Project; Activities, Roles, Artefacts; From Processes to Procedure and Process Modes
(see forum message with ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 6.5.: VL 04 "Procedure and Process Models"
Waterfall and Spiral; Prototype-based; Evolutionary, Incremental, Iterative; V-Model XT; Agile Processes; process metrics CMM(I) and SPICE
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 11.5.: Live Online Tutorial 2
- Thu, 13.5.: public holiday (ascension day)
- Tue, 18.5.: VL 05 "Requirements Engineering" - Exercise Sheet 3 online
Requirements Engineering basics: the RE problem, the software peoples' view on requirements; quality criteria for requirements and their (natural language) documentation
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 20.5.: VL 06 "Formal Methods for Requirements Engineering"
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 25.5.: whitsun break
- Thu, 27.5.: whitsun break
- Tue, 1.6.: VL 07 "Decision Tables"
One example of a formal notation for requirements and its use: decision tables (DT); formal definitions for completeness, consistency, determinism, etc.
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 3.6.: public holiday (corpus christi)
- Tue, 8.6.: Live Online Tutorial 3
- Thu, 10.6.: VL 08 "Use Cases and Scenarios, Live Sequence Charts" - Exercise Sheet 4 online
Scenarios and Anti-Scenarios for requirements analysis; notations User Story, Use Case, Use Case Diagram, first half of Sequence Diagrams (abstract syntax, cuts and firedsets); Second half of the 'Sequence Diagram' story (TBA construction)
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 15.6.: VL 09 "Live Sequence Charts Cont'd & RE Wrapup" - Exercise Sheet 4 online (submit via ILIAS)
LSCs and software; Requirements Engineering wrap-up
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 17.6.: VL 10 "Structural Software Modelling I"
Software Architecture; Views and viewpoints; Class Diagrams
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 22.6.: Live Online Tutorial 4
- Thu, 24.6.: VL 11 "Structural Software Modelling II" - Exercise Sheet 5 online (download additional materials and submit via ILIAS)
Partial vs. Complete Object Diagrams, Proto-OCL
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 29.6.: VL 12 "Behavioural Software Modelling"
Communicating Finite Automata; Uppaal Demo; Uppaal Query Language
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 1.7.: VL 13 "UML State Machines, MBSE/MDSE, Design Principles"
CFA "at work"; MBSE/MDSE; Implementing CFA; an outlook on UML Statemachines; Principles of Software Design: Modularisation, information hiding, data encapsulation etc.
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 6.7.: Live Online Tutorial 5
- Thu, 8.7.: VL 14 "Architecture & Design Patterns, Software Quality Assurance" - Exercise Sheet 6 online (download additional materials and submit via ILIAS)
Architectural patterns (layers, pipeline, MVC); Design Patterns; Test Case, Test suite, Pass/Fail, true/false Positives and Negatives
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 13.7.: VL 15 "Testing"
Coverage measures, Model-based Testing
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Thu, 15.7.: VL 16 "Software Verification"
Notions of correctness; Formal verification of software: the Hoare calculus; Software Model-Checking, VCC Demo
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream). - Tue, 20.7.: Live Online Tutorial 6
- Thu, 22.7.: VL 17 "Wrapup & Questions"
Runtime Verification; Review; Lecture recap and time for questions
(Slides (with annotations of 2019), 2-up, 6-up, Recording: ILIAS Download + Stream).
Links & Literature
- Software Engineering Textbooks
- Ludewig, J. and Lichter, H. (2013). Software Engineering. dpunkt.verlag, 3. edition.
Main inspiration for the lecture; unfortunately only available in German. Available as e-Book via UB. - Sommerville, I. (2010). Software Engineering. Pearson, 10. edition.
The international "classic". Available as e-Book via UB. (Book also available in German.) - Balzert, H. (2009). Lehrbuch der Softwaretechnik: Basiskonzepte und Requirements Engineering. Springer Spektrum, 3. edition.
The german "classic", part 1. Available as e-Book via UB. - Balzert, H. (2010). Lehrbuch der Softwaretechnik: Entwurf, Implementierung, Installation und Betrieb. Springer Spektrum, 3. edition.
The german "classic", part 2. Avaliable as e-Book via UB. - Bjørner, D. (2006). Software Engineering 1 - Abstraction and Modelling. Springer.
One of the few formal methods textbooks, part 1. - Bjørner, D. (2006). Software Engineering 2 - Specification of Systems and Languages. Springer.
One of the few formal methods textbooks, part 2. - Bjørner, D. (2006). Software Engineering 3 - Domains, Requirements, and Software Design. Springer.
One of the few formal methods textbooks, part 3.
- Ludewig, J. and Lichter, H. (2013). Software Engineering. dpunkt.verlag, 3. edition.
- Introduction
- Bauer, F. L. (1971). Software Engineering. In: IFIP Congress (1), pages 530-538.
Historic (type-writer typed) lecture notes by F. L. Bauer, one of the software engineering pioneers who is said to have brought up to the term 'software engineering' on the NATO Science Committee meeting in Garmisch, 1968, in response to the 'software crisis'. - Bjørner, D. and Havelund, K. (2014). 40 years of formal methods. . Presentation slides, UNSW, Sydney, 19. May 2014.
A brief introduction of the term "formal methods", its historical and present obstacles and hindrances, and an outlook. - Buschermöhle, R. et al. (2006). success - Erfolgs- und Misserfolgsfaktoren bei der Durchführung von Hard- und Softwareentwicklungsprojekten in Deutschland. Version 1.1 (source site).
A wealth of empirical data with a thorough evaluation wrt. a set of hypothesis on correlations of factors in software engineering. - Jones, C. B. et al., editors (2011). Dependable and Historic Computing - Essays Dedicated to Brian Randell on the Occasion of His 75th Birthday, volume 6875 of LNCS, Springer.
Timeless insights on software engineering from the early days, including an article by software engineering pioneer D. L. Parnas and the dinner talk by H. Kopetz. Available as e-Book via UB. - Most ISO/IEEE/etc. standards are unfortunately not freely available.
- Lamport, L. (2015). Who Builds a House without Drawing Blueprints?. CACM; 58(4): 38-41.
A somewhat polemic essay arguing for better planning in software engineering by 2013 ACM Turing Award winner (and LaTeX author) Leslie Lamport; not so far off from our approach to the software engineering lecture...
- Bauer, F. L. (1971). Software Engineering. In: IFIP Congress (1), pages 530-538.
- Project Management, Process Models, Metrics
- Brooks, F. P. (1996). The Mythical Man-Month - Essays on Software Engineering, Anniversary Edition. Addison-Wesley.
Some say "if you want to read only one book on the management of software development projects, let it be this" (without being the author or otherwise sponsored by the publisher). An e-Book of the 1st edition from 1974 is freely available here. - Douglass, B. P. (1999). Doing Hard Time, Addison-Wesley.
Spiral-shaped development process using formal modelling and analysis especially for (safety) critical, reactive, timed systems. - Wheeler, D. A. (2006). The Linux Kernel: It’s Worth More!
A COCOMO estimation of effort for the Linux kernel 2.6. Article includes a link to the used tool SLOCCount. - Karn, J. S., & Cowling, A. J. (2005). A Study into the Effect of Disruptions on the Performance of Software Engineering Teams. In the Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering, (ISESE 2005).
- Behfar, K. J., Peterson, R. S., Mannix, E. A., Trochim, W.M. (2008). The critical role of conflict resolution in teams: a close look at the links between conflict type, conflict management strategies, and team outcomes. J Appl Psychol.; 93(1):170-88. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.93.1.170.
- V-Modell XT Authors (2006). V-Modell XT, Version 1.4.
The V-Modell XT reference document (in German); an English document for V-Modell XT, version 1.3, is available on the same homepage. A tool to support tailoring is available here.
(Version 2.0 (in German); may not be subject of the lecture since it seems not to have an English translation so far.) - CMMI Product Team (2010). CMMI for Development, Version 1.3.
Definition of the CMMI-DEV process metrics. German translation is available here. An introdution to the appraisal procedure is available here.
- Brooks, F. P. (1996). The Mythical Man-Month - Essays on Software Engineering, Anniversary Edition. Addison-Wesley.
- Requirements Engineering, Live Sequence Charts
- Rupp, Ch., die SOPHISTen (2014). Requirements-Engineering und -Management. Hanser.
An extensive and comprehensive discussion of all aspects of Requirements Enginering, from formal notations, over quality criteria, recommendations for natural language requirements, to psychological aspects like human perception and conflicts among clients, which may show up during requirements engineering. The book's content builds on the main author's experience as general manager of SOPHIST GmbH, a company offering Requirements Engineering. Unfortunately only available in German. But: Available as e-Book via UB. - Damm, W., Harel, D. (2001). LSCs: Breathing Life into Message Sequence Charts. FMSD; 19(1): 45-80, Kluwer Academic Press.
The original work on Life Sequence Charts. - Klose, J. (2003): Live Sequence Charts - A Graphical Formalism for the Specification of Communication Behavior. PhD thesis, Carl von Ossietzky Universität Oldenburg.
The original work on the TBA-semantics of LSCs as used in the lecture. - Typesetting Live Sequence Charts: lsc.sty on CTAN (and included in TeX Live).
- Architecture & Design, Modelling
- Jacobson, I. (1992). Object-Oriented Software Engineering: A Use CASE Approach. Addison-Wesley.
By the inventor and early advocate of use cases and use case diagrams, which were later included in UML. 20 years old, odd-looking notation, yet the basic messages remain valid. - Kastens, U., Kleine Büning, H. (2014). Modellierung - Grundlagen und formale Methoden, Zweite Auflage, Carl Hanser Verlag.
General Discussion of Modelling, not focusing on UML, but also considering plain set-theory, graphs, Petri nets, and their use for modelling tasks. - Buschman, F., Beunier, R., Rohnert, H., Sommerlad, P., Stal, M. (1996). Pattern-Oriented Software Architecture, Volume 1, A System of Patterns. Wiley.
Actually closer to the content of Lecture 14 than the (more famous) standard textbook on design patterns (Gamma et al.) The concrete examples may provoke nostalgic feelings ("this sounds soo early 90s of the last century") but the basic messages still hold. Available as e-Book via UB. - UML
- B. Dobing, J. Parsons: How UML is used, Communications of the ACM, 49(5):109-114, 2006.
This survey supports the relevance of our choice of diagrams to be considered in the lecture. - OMG (2011). Unified Modeling Language: Infrastructure. Version 2.4.1.
The UML standard, basic concepts. May take some getting-used-to. - OMG (2011). Unified Modeling Language: Superstructure. Version 2.4.1.
Defines all the diagrams using concepts from the infrastructure document. - B. Oesterreich: Analyse und Design mit UML 2.1, 8. Auflage, Oldenbourg, 2006.
Standard introduction into UML notation (only informal semantics). - H. Stoerrle: UML 2 fuer Studenten, Pearson Studium Verlag, 2005.
And another one of the like.
(avaible as e-book via UB) - OMG (2014). Object Constraint Language. Version 2.4.
Our Proto-OCL semantics is inspired by Appendix A (finally something more formal...). - Kleppe, A., Warmer, J. (2004). The Object Constraint Language. 2nd Edition, Addison-Wesley..
A more palatable presentation of OCL.
- B. Dobing, J. Parsons: How UML is used, Communications of the ACM, 49(5):109-114, 2006.
- Formal Verification
- Apt, K.R., Olderog, E.-R. (1994). Programmverifikation. Springer-Verlag.
The formal verification part of Lecture 15 is following the thorough presentation in this (highly recommendable) book. Also available in English. - (2015) The VCC Manual.
A draft document to become a manual for VCC. For the exercises, it should not be necessary to revert to this document too much, the content of the lecture should be sufficient. - Cohen, E., Hillebrand, A., Tobies, S., Moskal, M., Schulte, W. (2015). Verifying C Programs: A VCC Tutorial. Technical Report.
A tutorial on VCC, distributed with the VCC sources. Again: for the exercises, you should not need much more than discussed in the lecture. We're only touching the surface of VCC. - Miscellaneous
- O. Laitenberger, C. Atkinson: Generalizing Perspective-based Inspection to handle Object-Oriented Development Artifacts, In: Proc. ICSE '99, 494-503, IEEE CS-Press.
Reading techniques philosophy. - G. H. Travassos, F. Shull, J. Carver, V. R. Basili: Reading Techniques for OO Design Inspections, Technical Report CS-TR-4353, University of Maryland, 2002.
Concrete reading techniques.
- O. Laitenberger, C. Atkinson: Generalizing Perspective-based Inspection to handle Object-Oriented Development Artifacts, In: Proc. ICSE '99, 494-503, IEEE CS-Press.

